Potassium Bicarbonate (KHCO₃): Comprehensive Guide to Industrial, Chemical, and Mining Applications

Potassium bicarbonate (chemical formula KHCO₃), also known as potassium hydrogen carbonate, is a white crystalline powder that is odorless and highly soluble in water. Its aqueous solution is mildly alkaline. As a single potassium salt, it consists of potassium ions (K⁺) and bicarbonate ions (HCO₃⁻), with a molecular weight of approximately 100.12 g/mol. When heated, potassium bicarbonate decomposes to release carbon dioxide and water, converting into potassium carbonate. This thermal decomposition behavior gives it particular value in industrial and chemical manufacturing processes.
Sodium Carbonate Anhydrous: Overview and Industrial Applications

Sodium Carbonate Anhydrous, with the chemical formula Na₂CO₃, is a widely used inorganic alkaline compound. It appears as a white or off-white, odorless crystalline powder that dissolves easily in water, producing a strongly alkaline solution. In the chemical industry, sodium carbonate anhydrous is also commonly referred to as soda ash. It is one of the most important basic chemical raw materials, available in grades ranging from industrial grade to high-purity reagent grade to meet diverse application requirements.
2026: A Pivotal Year for China’s Chemical Industry with Innovation and High-End Growth in Focus

Analysts indicate that 2026 is poised to be a pivotal year in the cyclical development of China’s chemical industry. The growth engines for China’s chemical industry are expected to increasingly derive from structural product development and deeper international market engagement. Stable development in traditional sectors will continue to safeguard consumption demand for basic chemicals, while rising demand for high-end chemical products — such as premium coatings, modified plastics, and high-end polyolefins — will support sustained growth.
High-Grade Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate Monohydrate: Why It’s Essential for Food, Pharma & Labs

From stabilizing the texture of your favorite processed foods to balancing pH levels in pharmaceutical formulations and laboratory buffers, Sodium Dihydrogen Phosphate plays a quiet yet essential role across various industries. Yet, it’s often overlooked, despite being a behind-the-scenes hero in countless processes. Whether you’re a procurement professional, a quality analyst, or simply curious about the chemicals shaping our world, understanding NaH₂PO₄·H₂O can help you make smarter sourcing and application decisions.
Mining Chemicals Market Reaching USD 20.3 Bn by 2034
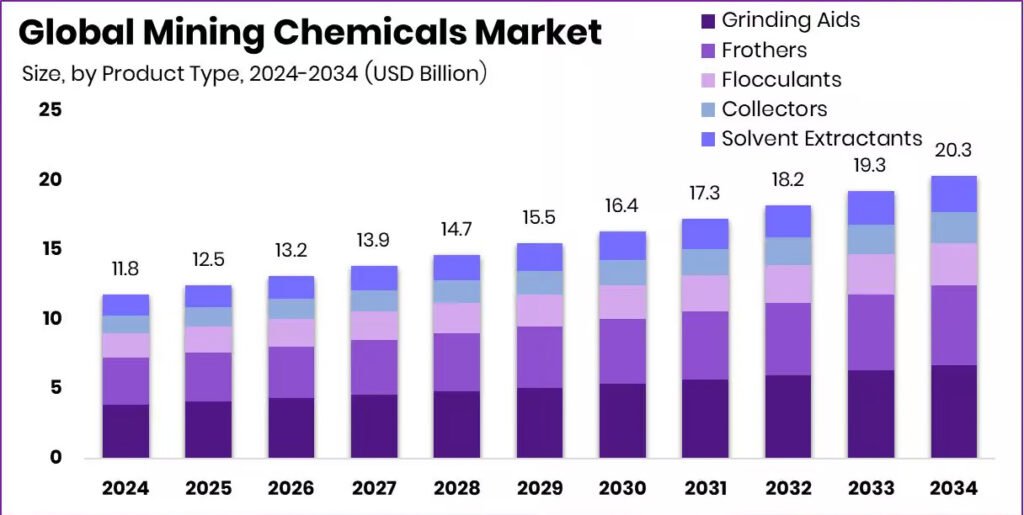
The Global Mining Chemicals Market is growing fast, driven by increasing demand for minerals and metals across industries like construction, automotive, and electronics. In 2024, the market was valued at USD 11.8 billion, but it is expected to reach USD 20.3 billion by 2034, growing at a steady CAGR of 5.6%.These chemicals play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency and recovery rates across the global mining sector.
Calcium Chloride Anhydrous: The Unsung Workhorse of Modern Industry

When it comes to chemicals that quietly make a big difference in our daily lives, Calcium Chloride Anhydrous deserves more recognition. From melting ice on winter roads and stabilizing construction projects, to extending the shelf life of food and keeping industrial processes running smoothly, its applications are both broad and vital. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at what Calcium Chloride Anhydrous is, its defining properties, and why businesses across diverse industries depend on it.
Magnesium Sulphate Heptahydrate: Properties, Benefits & Diverse Applications

Magnesium Sulphate Heptahydrate plays a vital role in countless industries. Commonly recognized in its refined form as Epsom Salt, this seven-hydrate crystal is far more than a household remedy — it’s a critical raw material in pharmaceuticals, food processing, agriculture, water treatment, and industrial operations. In this guide, we’ll explore its chemical profile, physical characteristics, practical uses, and the reasons why quality and compliance are essential when sourcing this versatile compound.
Natural and Versatile Chemical Raw Material — Pine Oil

Pine oil is a terpene alcohol mixture extracted from parts of pine trees—typically Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris). Its primary components include α-terpineol, β-terpineol, and other cyclic terpene phenols and olefins. Pine oil is typically graded into 50%, 65%, 70%, and 85%, indicating the percentage of terpene alcohol content. Higher grades offer increased purity, stronger fragrance, and enhanced disinfecting performance.
Do You Know Methyl Isobutyl Carbinol (MIBC)?

Methyl Isobutyl Carbinol (MIBC), also known by its chemical name 4-Methyl-2-pentanol (CAS No. 108-11-2), is a colorless to pale yellow transparent branched secondary alcohol with a mild alcohol-like odor. As a key chemical raw material in multiple fields, has clear physical and chemical advantages and application prospects, with outstanding characteristics of environmental protection, low toxicity, high efficiency and practicality.
Sodium Nitrate: Properties, Applications, and Safe Handling

Sodium nitrate (chemical formula: NaNO₃), commonly known as “Chile saltpeter”, is a white powder or colorless crystal. It has a molecular weight of approximately 85, a density of 2.257 g/cm³, and a melting point of about 306.8 ℃.Sodium nitrate is often used as a component of mining explosives. In addition, its application as an oxidizing flux and clarifying agent in the glass industry is also related to mining.

