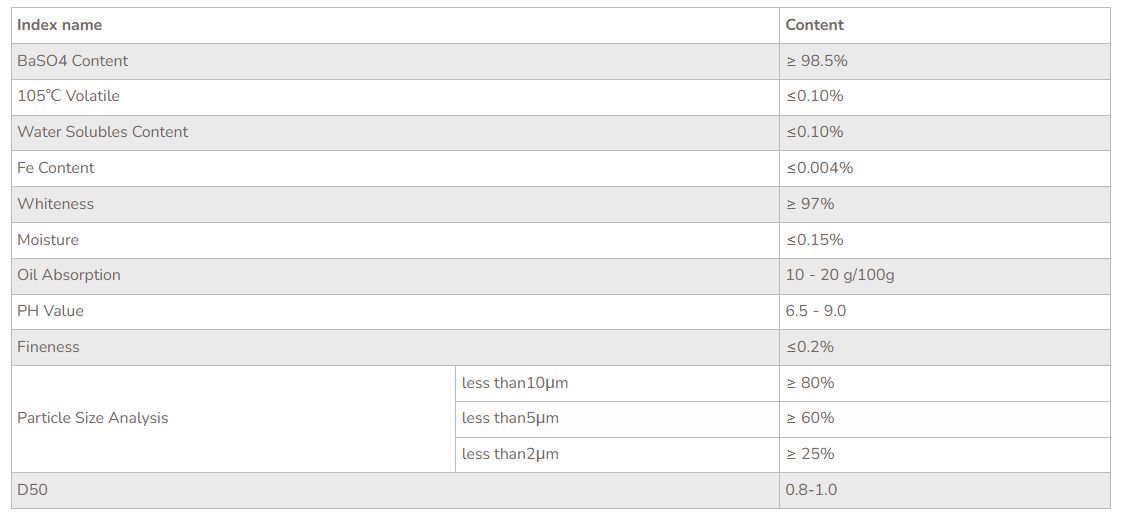
Barium Sulfate
Barium sulfate (or sulphate) is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula BaSO4. It is a white crystalline solid that is odorless and insoluble in water. It occurs as the mineral barite, which is the main commercial source of barium and materials prepared from it. Its opaque white appearance and its high density are exploited in its main applications.Barium sulfate is reduced to barium sulfide by carbon. The accidental discovery of this conversion many centuries ago led to the discovery of the first synthetic phosphor.The sulfide, unlike the sulfate, is water-soluble.