Preparation of high purity manganese dioxide: ferrous sulfate has strong reduction, the main component of soft anite is MnO2, and MnO2 has strong oxidation under conditions, so under sexual conditions, they can be mixed together to prepare high purity manganese dioxide.
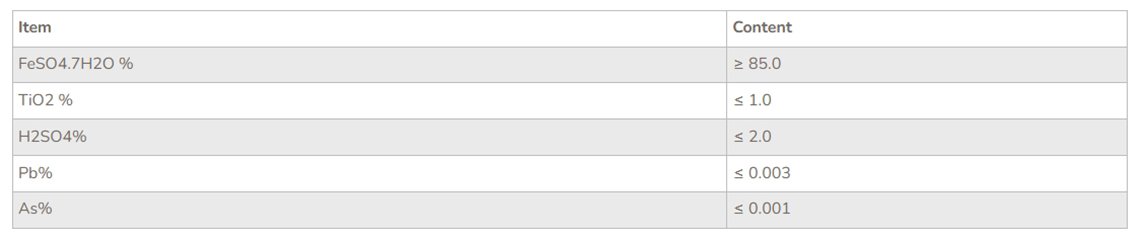
Refined ferrous sulfate: there are many methods to purify ferrous sulfate, such as recrystallization method, hydrolysis precipitation method, ultrafiltration method, etc. After purification, ferrous sulfate can be directly used as the starting raw material for subsequent preparation of high quality iron oxide, and can be directly used as the starting raw material for water purification agent.
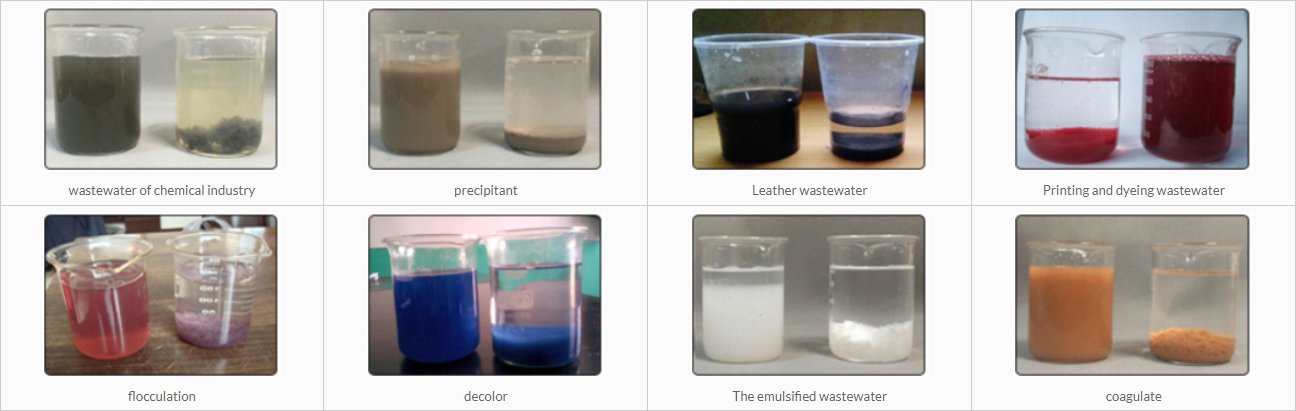
Preparation of polyferric sulfate: flocculation is a water treatment technology widely used at home and abroad. The quality of flocculation effect depends on the performance of flocculant. Polymeriron sulfate is a new and efficient iron inorganic polymer flocculant, is a kind of basic iron sulfate polymer. With the characteristics of short condensation time and good settlement performance of catkins, the removal rate of wastewater turbidity can reach more than 95%, and the removal rate of wastewater color can reach 80%.
Preparation of iron oxide red: iron oxide red, is a red pigment, its composition is Fe2O3, namely hematite. Non-toxic, insoluble in water, has a very high covering force and coloring force, its light resistance, heat resistance, alkali resistance and dilute acid resistance are very good. Iron sulfate can be used to prepare iron oxide red, to achieve waste reuse.
Preparation of iron oxide yellow: iron oxide yellow, is a yellow pigment, namely needle iron ore, its light resistance, pollution turbidity gas resistance and alkali resistance are very strong, but the acid resistance is poor. The preparation of ultrafine transparent iron oxide yellow with ferrous sulfate is ideal.
Nano iron oxide: nano iron oxide is transparent iron oxide, has the advantages of high transparency, good dispersion, bright color, in the paint, ink, plastics and other industries have a wide range of uses, is a new variety with unique properties of iron pigments. With ferrous sulfate and industrial grade ammonium bicarbonate as raw material, ferrous iron oxide can be produced by liquid phase method.
Metal anticorrosion: in the straight water cooling system, a small amount of ferrous sulfate can be added to the water inlet of the condenser to form a layer of iron oxide protective film on the inner surface of the copper alloy tube, so as to prevent or reduce the corrosion of the alloy tube.
Others: ferrous sulfate can also be used to make blue and black ink and leather dyeing, as well as photography and printing plate making. It can also be used as an etcher for aluminum devices, a catalyst for polymerization in the chemical industry, reagents in chemical analysis, wood preservatives, and therapeutic drugs for iron deficiency anemia.